Image: homvee.acf.gov
by Marie Cohen
Home visiting has been a highly popular intervention for the prevention of child abuse and neglect and for addressing a much broader set of social problems as well. But the research has never supported the efficacy of home visiting programs as a whole for improving child and family outcomes. The latest study of four popular home visiting programs found that all these programs have negligible impacts after five to seven years. But there was no hint of this message in the government’s press release or the report itself. The bipartisan belief in home visiting is prevening a needed examination of home visiting’s impact and the level of resources devoted to it.
A Brief History of US Home Visiting
While home visiting has existed since Elizabethan times in England, its history in the U.S. began in the late nineteenth century with charities seeking to address urban poverty by changing the behavior of poor families. While it is now considered to be the solution to a number of different social problems mostly related to poverty, modern home visiting was conceived as a way to prevent child abuse and neglect. Publication of Henry Kempe’s The Battered Child in 1968 brought about the recognition of child maltreatment as a national problem. To address child abuse, Kempe called for universal prevention through a network of home health visitors. Inspired by Kempe, Hawaii’s Healthy Start Project (HSP) began in 1975. In 1977, David Olds began testing his Nurse Home Visiting program in Elmira, New York. The first Parents as Teachers program was created in 1991. In 1992, the National Committee to Prevent Child Abuse (now Prevent Child Abuse America) rolled out Healthy Families America (HFA).
In 1993, the Future of Children, an influential academic journal produced by Princeton University and the Brookings Institution until 2021, devoted an issue to home visiting. In the summary article, the authors cautioned that the research so far was limited and had mixed results, but opined that the results were “promising enough” to recommend the expansion of existing programs and the continuation of evaluation efforts. Home visiting programs burgeoned in the wake of that issue, with funding from federal, state, and foundation sources.
In 1999, The Future of Children released its second issue on home visiting, containing evaluations of six demonstration programs. The results were sobering. In their analysis of all six studies, Deanna Gomby and colleagues concluded that “[I]n most of the studies described, programs struggled to enroll, engage and retain families. When program benefits were demonstrated, they usually accrued only to a subset of the families originally enrolled in the programs, they rarely occurred for all of a program’s goals, and the benefits were often quite modest in magnitude.” The one exception was the Nurse Home Visiting Program, (now Nurse-Family Partnership), which differed from the other programs in being delivered by nurses rather than paraprofessionals, and which produced some sizable impacts on child abuse and neglect and second births to mothers.
But the home visiting juggernaut was already in motion. Programs continued to grow, funded by multiple sources, and most of the growth was not in the most promising (and expensive) Nurse-Family Partnership. The National Center to Prevent Child Abuse, renamed Prevent Child Abuse America in 1999, made HFA its signature program despite the lack of evidence that it prevents child abuse. According to the National Home Visiting Resource Center, “evidence-based home visiting was implemented in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, 5 territories, 32 Indigenous communities, and 65 percent of U.S. counties” by 2024. These programs reached over 284,000 families through more than three million home visits in that year, and another 70,000 families were reached by 11 “emerging models.” Of the more than three million home visits provided, approximately 14 percent were provided virtually, down from nearly 23 percent in 2024, as services gradually returned to in-person after the pandemic. Today, there are multiple home visiting programs with different target groups, curricula, goals, and personnel. In addition to the 24 models recognized by the federal government, there are an unknown number of “emerging models” which have not yet earned the label of “evidence-based.”
Undaunted by the scant evidence of success, Congress established, with bipartisan support, the Maternal, Infant and Early Childhood Home Visiting Program (MIECHV) as part of the Affordable Care Act of 2010. The goals of the program are to improve the health of mothers and children, prepare children for success in school, improve families’ economic well-being, connect families to other resources in the community, prevent crime and domestic violence and prevent child injuries, abuse and neglect. The funds can be used to implement any one of 24 models that meet the eligibility criteria established by HHS’ Administration for Children and Families (ACF). An evaluation of this program was required by the legislation.
Home visiting programs also became a popular intervention in child welfare with the growing emphasis on keeping children with their families. This began in 1994 with the Title IV-E waivers and continued with the Family First Prevention Services Act (FFPSA), signed by President Trump in 2018. FFPSA allowed states to use Title IV-E funds, formerly reserved for foster care and subsidized adoptions, to support children and families and prevent foster care placements through in-home parent skill-based programs, as well as mental health, drug treatment and kinship navigator services. Programs had to be approved by the new Title IV-E Prevention Services Clearinghouse as “evidence-based” before they could be included in a state’s Family First Prevention Services Plan. According to a research brief from Chapin-Hall at the University of Chicago, at least one home visiting model was included in the Family First Prevention Plans in 28 states as of April 2023. Most commonly included were Parents as Teachers (28) and Healthy Families America (23), with Nurse Family Partnership in third place with 15 programs, and SafeCare in fourth with seven programs.
Home visiting also became popular in growing efforts by child welfare agencies to invest in preventing child abuse and neglect before it occurs, or at least before a family comes to the attention of child protective services. A small source of federal funds, the Community Based Child Abuse Prevention Program (CBCAP), was established by Congress in 1996 to fund such prevention programs and is commonly used to fund home visiting as well.
The bipartisan enthusiasm for home visiting has been unwavering. Created under Obama, MIECHV has been supported by every succeeding administration. Total federal funding on this program is slated to increase from $500 million in 2023 to $800 million in 2027.Earlier this year, the Senate even passed (unanimously) a bipartisan resolution designating April 21 through April 25, 2025 as National Home Visiting Week. Even the Trump Administration has heartily endorsed the home visiting. Yet, the much-vaunted evidence for the value of home visiting really consists of a series of modest impacts affecting different outcomes, often based on less reliable indicators like self-reports, and dwarfed by a sea of findings of no effect. Even the one program (Nurse-Family Partnerhip), that had the most promising early resultsm has no stood up to recent replications–though additional trials with the population that seems to benefit most may be warranted.
Home visiting program evaluations
There have been multiple studies of home visiting programs, including both randomized controlled trials (RCT’s) and comparison group studies, and together these studies have generated hundreds of papers. Therefore, Child Welfare Monitor (CWM) drew from a summary of research on Nurse-Family Partnership from the Arnold Ventures Social Programs that Work website; the evidence assembled on the website of the Title IV-E Prevention Services Clearinghouse for Healthy Families America, Parents as Teachers, and SafeCare; and the Home Visiting Evidence of Effectiveness (HomVEE) Review conducted by the Administration on Children and Families of HHS for Early Head Start Home-Based Option. CWM consulted the original studies as needed, focusing on RCT‘s because randomization is the best way to rule out selection bias as the explanation for any differences between the intervention group and the control group. Otherwise, one cannot know whether the group that participated in the program differed in significant but unmeasured ways from the members of the comparison group. Appendix I includes more details about the program evaluations. Appendix II focuses on the challenges in measuring child abuse and neglect and what the research suggests.
Nurse-Family Partnership
Nurse -Family Partnership (NFP) connects first-time mothers and their babies with a specially trained nurse, who works with the mother and child from early in the pregnancy through the child’s second birthday. It differs from other models in using registered nurses to deliver the visits, making it more expensive and dependent on a scarcer group of providers. Nurse Family Partnership (NFP) has been the subject of RCT‘s in Elmira, NY (launched in 1988); Memphis, TN (launched in 1990), Denver, CO (1994) and in a larger statewide trial in South Carolina that started in 2016. It has also been tried internationally in British Columbia, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and Germany; though the differences between populations and systems make these results less applicable to the United States, they can be seen as suggestive. The participants in the demonstrations were all first-time mothers but other criteria for inclusion varied by study. Among the effects that were replicated in two or more of the studies identified by the Arnold Ventures’ Social Programs That Work website were reductions in medical treatment for injuries and accidents in Elmira and Memphis), reductions in subsequent births to mothers in their late teens and early twenties (in Elmira, Denver, and Memphis), and an improvement in cognitive or academic outcomes for the children of mothers with lower psychological resources, like intelligence, mental health, and self-confidence (in Memphis and Denver). There were few significant impacts on children’s emotional and behavioral outcomes and mothers’ life trajectories in terms of employment, income and crime, and those impacts were not repeated in more than one study.
A recent scaled-up NFP replication in South Carolina was disappointing, producing no significant positive effects on any of the three primary outcomes studied: the rate of adverse birth outcomes, mothers’ rate of subsequent births within 21 months, and child health, measured as “a composite of mortality or health care utilization associated with major injury or concern for abuse or neglect.” Nor did the researchers find any significant improvements for a prespecified subsample of “socially vulnerable families” that were similar to the families for which earlier studies found positive impacts. There were also no significant findings for the secondary outcomes, which related to healthcare utilization. These results were sobering, and the researchers suggest that the rapid scaling up of the program and the broader population served may have contributed to the weaker results. David Olds, the founder of NFP, suggests1 that the program’s effectiveness was affected by the relative inexperience of the nurses (due to the rapid implementation), the use of impersonal recruitment methods (unlike Elmira and Memphis, where nurses personally recruited mothers in clinic waiting rooms), and the relatively more advantaged clientele. The program included any pregnant woman who qualified for Medicaid in South Carolina, which funded 46 percent of births in that state in 2023 and includes women up to 200 percent of the poverty level. So it was a less disadvantaged group than was included in the other US demonstrations, and earlier studies suggested that the more disadvantaged benefited more from this program.2 Thus, further study of NFP with a highly disadvantaged population should be considered.
Healthy Families America (HFA)
Healthy Families America, an initiative of the national organization, Prevent Child Abuse America, is a flexible program that allows local communities to choose their eligibility criteria, parenting materials, and staff. Services last for a minimum of three years and up to five years. Based on three RCTs of Healthy Families America, the Title IV-E Prevention Services Clearinghouse counted 18 favorable “contrasts” (their term for comparisons between the intervention and control groups) compared to four unfavorable contrasts and 211 contrasts displaying no effect. Among the 18 favorable contrasts, 11 were on self-reports of maltreatment or child behavioral and emotional functioning. Of the other impacts, all were from only one RCT. Many outcome categories showed no favorable impacts. These included child safety measured by administrative reports; child safety based on injuries, Emergency Room use or hospitalizations; child permanency based on out-of-home placements; child social functioning; child physical development and health; parent/caregiver substance abuse; and economic and housing stability. One of the four RCT‘s (Healthy Families Oregon) showed no positive impacts at all.
Parents as Teachers
Parents as Teachers is delivered by “parent educators” who work with families from pregnancy through kindergarten. The Clearinghouse identified one American RCT of this program, one RCT from Switzerland, and one matched comparison group study. The one US RCT, which evaluated two separate demonstrations in California, found that PAT had “little effect on parenting knowledge, attitudes or behaviors as measured in these demonstrations. Nor were significant effects noted on child health or health care.” The demonstration did find small positive effects (a two-month gain at the age of three) on “self-help development” in one of the two sites but no significant effects on cognitive development at either site. In the Swiss study, the clearinghouse found one significant effect on one of two measures of the child’s expressive language.
SafeCare
SafeCare is a brief home visiting model that is delivered in 18 one-hour sessions. SafeCare is designed for parents and caregivers of children birth through five who are either at-risk for or have a history of child neglect and/or physical abuse. It was included in the Title IV-E Prevention Plans of seven states in April 2023. The contrasts reported by the Clearinghouse include only one favorable effect–on foster care placement–based on a matched comparison group study and not an RCT and one unfavorable effect (on child welfare reports), along with 19 findings of no effect.
Early Head Start-Home-Based Option
Early Head Start Home-Based Option provides weekly visits to pregnant women, infants, and toddlers until the child is three years old. The goal is to promote school readiness of young children by enhancing their cognitive, social and emotional development. The federal reviewers of Early Head Start’s Home-Based Option used nine publications based on a large federal RCT of the program at 17 sites as well as the early results of the federal study of MCHIEV programs, which is described below. There were no favorable findings on maternal or child health; child maltreatment; or delinquency, family violence and crime. There were a few favorable impacts on child development and school readiness; positive parenting practices; and family economic self-sufficiency scattered among multiple findings of no effect. These effects were not consistent across age groups or outcomes where one would expect some alignment (like reading to children vs. reading at bedtime). These impacts appeared to be small, although the lack of standardized effect sizes complicates interpretation. In the final report on Early Head Start, the authors stated that at “the end of the program, when children were three, impacts were modest in size and Early Head Start children continued to perform below national norms on cognitive and language assessments.” By the time the children reached fifth grade, all but one favorable impact earlier reported was gone.
The MIHOPE Study
The legislation establishing the Maternal, Infant and Early Childhood Home Visiting Program (MIECHV) required an evaluation of the program in its early years. The study, named the Mother and Infant Home Visiting Program Evaluation (MIHOPE), included 88 local programs in 12 states and was carried out by an evaluation nonprofit called MDRC. All of the programs were based on one of the four models most commonly chosen by states in their initial MIECHV plans–Early Head Start Home-based Option, Healthy Families America, Nurse-Family Partnership, and Parents as Teachers. A total of 4,229 families enrolled in the demonstrations between 2012 and 2015. Strangely, even though the sample sizes were large enough to estimate the effects of each program model, the researchers opted to report findings for all four models taken as a whole, a decision that has been criticized by experts and funders because of the significant programmatic differences between the models. Early findings released in 2019 from when the children were 15 months old were disappointing. There was little difference between the experimental and control groups. About a third of the 63 outcomes measured were statistically significant and though most comparisons did favor the home-visited groups, the effect sizes were extremely small–too small to be of any practical significance. The authors reported that for most outcomes the effects were slightly smaller than the average effects found in past studies of the models (which were already modest).
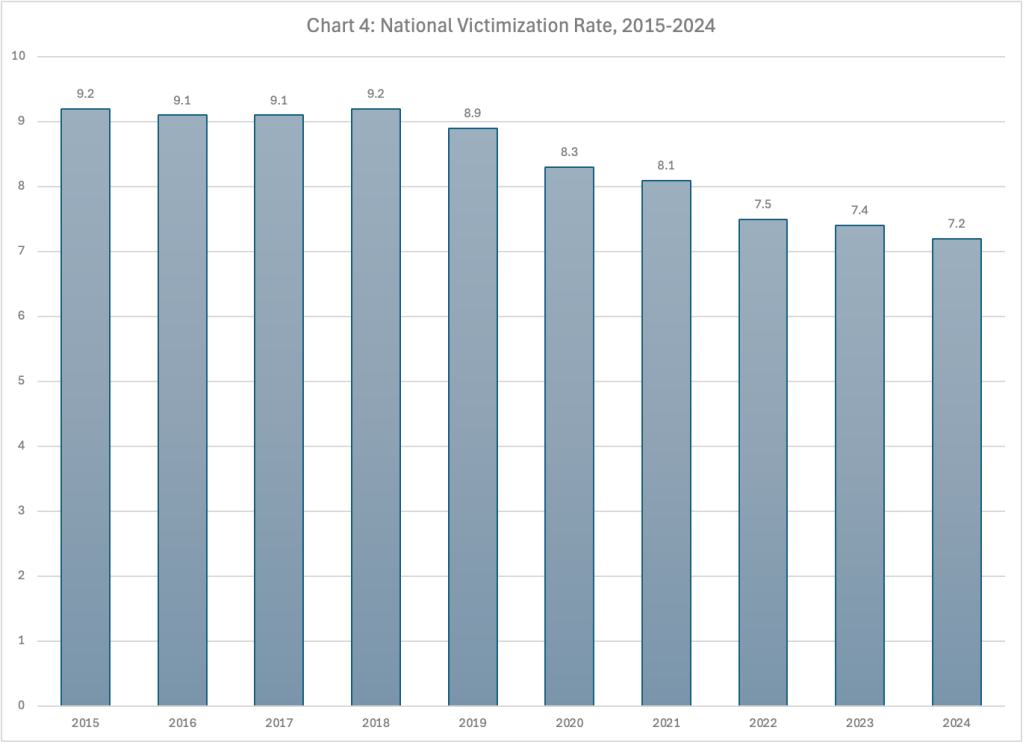
On September 11, 2025, the Administration on Children and Families released the long-term results of the MIECHV program evaluation conductd five to seven years after enrollment, when children were in kindergarten or first grade. Summing up their findings in a press release, ACF asserted that “MIECHV-funded home visiting significantly improved maternal and family wellbeing for participants five-to-seven years after enrolling in services…MIHOPE found statistically significant and positive effects of home visiting” for the five categories of maternal and family well-being outcomes. For the three categories of child outcomes, the researchers found “some evidence of positive effects,” but only one was statistically significant and positive.
Unfortunately, the researchers did not distinguish between a statistically significant effect and an effect which is large enough to be meaningful. A more sober analysis by the Coalition for Evidence-Based Policy shows that home visiting produced “negligible outcomes” for each of the eight expected impacts. The review points out that the average effect size across the six statistically significant or near-significant categories of effects was 0.03 – the equivalent of moving the average child or mother from the 50th to the 51st percentile. The study did not report model-specific effect sizes, but the reviewers noted that they are likely to be small or modest given that few reached statistical significance. It is also worth mentioning that many of the outcomes came from maternal answers to a caregiver survey, introducing the possibility of bias..
It is also concerning that the evaluation team at MDRC used a different analysis plan to assess impacts for the kindergarten study than it did for the earlier results. The new analysis plan was dated January, 2025 (but not released until May 2025). The new methodology combined all the 66 outcomes studied into eight new “research questions” some of the outcomes were included under more than one research question. The researchers chose to focus not on the significance of each individual impact, as was done in the earlier report. Instead, they decided to use a method called “omnibus testing” to compute an overall significance level for each research question.3 By choosing this method, they were able to find significant results (at the 0.10 level) for five of the eight research questions, where looking at each outcome would have shown only eight significant outcomes out of 86, or less than 10 percent of the outcomes. Since the new analysis plan was dated January 2025, it seems likely that it was developed after an analysis of the data (which was collected in 2021 and 2022) under the old plan yielded unsatisfactory results.4 The Imprint has published a more detailed critique of the MIHOPE study by Sarah Font and Emily Putnam-Hornstein called The Odd Bipartisan Effort to Oversell the Evidence for Home Visiting.
Why have home visiting programs been so unsuccessful at changing outcomes for most children and families?
As Deanna Gomby stated back in 1990, “home visiting programs have struggled to engage and retain families.” Research has documented low levels of enrollment and engagement of families at risk of maltreatment in voluntary services in general and home visiting in particular. According to the MIHOPE implementation report, 17 percent of the home visiting group never even received one visit, as compared to 12 to 22 percent in previous studies. All the models expected families to participate at least until the child’s second birthday, with services available for two or three years longer in three of the programs. Yet, only 46 percent of families were still participating in home visits 12 months after their first visit, consistent with previous research. On average, families who received at least one home visit went on to participate for an average of eight months. While participating, families received fewer visits than expected by the models in which they were enrolled. In the first 12 months, less than 60 percent of families received at least half of the visits prescribed by their model, a result consistent with prior research. Part of the problem might be that many people who need the kind of help that home visiting is designed to provide do not want to let a stranger into their home to scrutinize their parenting and family functioning. Child Welfare Monitor has heard in the District of Columbia and elsewhere that there is an oversupply of home visiting slots, with too few people wanting to participate.
Misleading Congress, the Media and the Public
Ever since the initial excitement about home visiting, there have been high hopes for this service delivery method and unwillingness among policymakers on both sides of the aisle to discard their hopes. At the same time, the federal government along with many advocacy groups, has endorsed a vision of “evidence-based practices” that asks only for a minimal number of statistically significant impacts, with no concern about the size of the impacts or the nature of the evidence–whether it is self-reported, self-contradictory, or unsupported by more than one study. As a result, studies that show only a few modest impacts that may be statistically significant but not meaningful in size or corroborated by other studies can be cited as evidence of program success.
Unfortunately, program evaluations are technical enough that readers who are not schooled in the intricacies of research methods are often forced to rely on the researchers’ interpretation of their findings. The usually well-informed Congressional Research Service has stated that “A large body of research suggests that some home visiting models or services can benefit children and their parents.” Less surprisingly, the press is easily misled. Due to lack of time or expertise in the intricacies of social science research, reporters often simply report what is in the press release announcing new research results. For example, the Imprint, a widely circulated outlet for child welfare content, repeated in its podcast the government’s misleading proclamation about good news from the MIHOPE study.
—–
No matter how painful the process, legislators, agency officials and advocates should remove their blinders about home visiting. It is time to phase out the MIECHV program. State and local governments should begin scaling down their home visiting programs and funneling the money to other uses that are currently underfunded. In this time of budget scarcity, it is time to stop throwing good money after bad. We need new ideas and meaningful evaluations that can bring about the implementation of programs that actually work. If money is being wasted on home visiting services that are not making a difference, or not even being used, surely there are better uses of these scarce funds.
Appendix I
In the absence of time to review the hundreds of publications on the Nurse Family Partnership Program, I used the excellent evidence summary on the Arnold Ventures Social Programs that Work website. For the studies of HFA, Parents as Teachers, and SafeCare, I relied mostly on the compilation of study results provided by the Title IV-E Prevention Services Clearinghouse. For Early Head Start, which was not included in the Clearinghouse, I used the Home Visiting Evidence of Effectiveness review conducted by the Office of Policy Research and Evaluation (OPRE) of the US Department of Health and Human Services.
Nurse Family Partnership
Each of the four U.S. RCT’s of NFP had a different population and eligibility criteria for participants. Elmira is in a small, semirural county in New York State which had the highest rate of child abuse and neglect in the state at the time of the study. In 1980, the community was rated the lowest Standard Metropolitan Statistical Area in the United States for economic conditions. Program participants In Elmira were either teens, unmarried, or low-income, and all were White. They were actively recruited by nurses at the prenatal clinic, private obstetricians’ offices, Planned Parenthood, schools, and other health and human services agencies. In Memphis, the program admitted pregnant women with no previous live births who did not have a chronic illness that might affect the fetus and who had at least two of the following risk factors: being unmarried, having less than 12 years of education, and being unemployed. Ninety-two percent of the women enrolled were Black, 98 percent were unmarried, 64 percent were eighteen years old or younger and 85 percent came from households with incomes at or above the poverty level. In Denver, women were recruited at any point in their pregnancy if they had no previous live births and either qualified for Medicaid or had no health insurance. Almost half of the two groups were Hispanic, another 35 percent were Caucasian, and 16-17 percent were Black. The South Carolina demonstration recruited pregnant women who were 15 years or older and eligible for Medicaid, which meant their incomes were less than two percent of the poverty level. The participants were mainly non-Hispanic Black (54.9 percent) and non-Hispanic White (35.0). In addition to enrolling a different population, each study looked at a different set of outcomes, and sometimes at different times as well, making it hard to compare the results. The findings of the demonstrations are summarized below.
- Child safety based on child welfare administrative reports: There was no statistically significant difference among confirmed child maltreatment reports between the experimental and control groups in Elmira. But there is some evidence that the Elmira program reduced child maltreatment among the participants who were most at risk, those who were teenagers, poor and unmarried. Among this group, 19 percent (or a total of eight) of the poor, unmarried teens had a verified maltreatment report compared to only one of their nurse-visited counterparts. But this effect was statistically significant at the p-0.7 level, not the standard level of 0.05. And there were no treatment-control differences in verified maltreatment reports during the two years after the program ended. However, the Elmira study did find a large impact on verified CPS reports when the children were 15; nurse-visited children had received on average of 0.29 verified CPS reports compared to 0.54 in the comparison group. This result is difficult to explain and one wonders if it was due to chance.This outcome was not examined in Memphis or Denver. The Netherlands study also found a large, statistically significant impact on child welfare administrative reports, where the researchers found that 11 percent of the visited children had a CPS report compared to 19 percent of the control group children during the first three years of their lives.
- Child safety based on health care for injuries and ingestions: Nurse visited children in Elmira had fewer emergency room visits for injuries and ingestions in their second year of life than the control group. (This was not measured during the first year, when they were less mobile and able to get into trouble. No effect size was provided). When they were between 25 and 50 months old, they had 40 percent fewer mentions for injuries and ingestions in their medical records and 45 percent fewer mentions of child behavioral or parental coping problems. In Memphis the researchers found that in the first two years of life, nurse-visited children had an average of 0.43 health encounters for injuries or ingestions compared to 0.56 for the control group, or 23 percent fewer encounters. They also spent an average of 0.04 days hospitalized for injuries and ingestions, compared to 0.18 days for the control group– a 78% decrease. A more recent evaluation of a large scale implementation of NFP in South Carolina found no difference between the experimental and control groups on child health, measured as “a composite of mortality or health care utilization associated with major injury or concern for abuse or neglect.” In the UK Study, there were no differences in the rates of emergency hospital visits for the experimental and control groups.
- Child wellbeing based on behavioral and emotional functioning: This outcome was not included in Elmira at two and four years. But there were large favorable effects on self-reported arrests and convictions for the Elmira children at age 15-19–a finding that was not reported anywhere else and was not matched by effects on other outcomes like high school graduation, teen pregnancy, engagement in work or school at 19, or self-reported substance use or welfare receipt, all of which could have been expected to covary with the arrests and convictions. So it is not clear whether these results occurred by chance. In Memphis there were no effects found on children’s reported behavioral problems at two years, nor were there any results on youth behavioral functioning when they got older. There were significant favorable effects on child emotional functioning in Denver at two years and four years. By ages six to nine in Denver, behavioral and emotional effects were consistently favorable but did not reach statistical significance at standard levels, perhaps because the sample size was not large enough.
- Child wellbeing based on cognitive functions and abilities: In Elmira there were no statistically significant cognitive effects on children in the first two years, although the researchers observed “improved intellectual functioning of nine to 11 points on the developmental tests for children from the highest risk families. Although only marginally significant statistically, the researchers observed that it is of clinical importance. Treatment effects in this range are consistent with those obtained for children of this age enrolled in intensive early childhood intervention programs aimed specifically at enhancing cognitive development.” In Memphis, there were no effects at two years on children’s mental development but there were substantial statistically significant effects on academic performance at age 12 for the children whose mothers were in the lower half of the sample on intelligence, mental health and self-confidence. In Denver, there were favorable effects on the cognitive development of children born to mothers with low psychological resources in the two-year follow-up. This group also did better cognitively at ages six to nine but the findings only occasionally reached statistical significance and may be due to attrition differences between the intervention and control groups. But at age 18 there were “sizable, significant” effects on two of three cognitive outcomes for this subgroup in Memphis. Cognitive effects were not studied for Elmira or Denver 18-year-olds.
- Maternal life course: When the children were aged 15, the Elmira study found that nurse-visited mothers had 19 percent fewer births than control mothers, an average of 1.3 births compared to 1.6. In Memphis, the mothers had 16 percent fewer births in the first six years of the program. They had caught up by the time the children were 12, but the increase in birth spacing is still a significant favorable outcome. In Denver, home-visited women had fewer subsequent pregnancies (29 percent vs. 41 percent) and births (12 percent vs. 19 percent) by their children’s second birthdays. There was no impact on the rate of second pregnancies after two years in the South Carolina, British Columbia, and UK studies. Where reported, there were no effects on adverse birth outcomes, maternal employment, likelihood of partnership or marriage with the child’s father, substance abuse, psychological distress or foster care placements (mentioned only in Memphis).
Healthy Families America
The contrasts presented by the Title IV-E. Clearinghouse were based on four RCT’s that were rated highly for design and execution by clearinghouse staff. The results of each RCT are based on multiple research papers published for each major study. Reviewing the Clearinghouse’s tabulation of the data, and sometimes comparing it to the actual publications to which it referred, raised several questions about the overall effectiveness of the program:
- Child safety measured by child welfare administrative reports: There were no favorable or unfavorable outcomes, as compared with 43 contrasts showing no statistically significant effect.
- Child safety, based on maternal self-reports about whether they maltreated their children: There were five favorable contrasts, 38 contrasts with no effect, and one unfavorable contrast. It is hard to be confident about the validity of self-reports of maltreatment, as one could easily imagine the program participants having learned more about what to report, and under-reporting behaviors (such as spanking) that they had been taught were undesirable. The large number of contrasts with no effect is worth noting.
- Child safety based on injuries needing medical care, hospitalizations, and emergency use: There were no favorable or unfavorable impacts and 11 contrasts showing no effect.
- Child permanency based on out-of-home placements: There were six contrasts showing no effect, and none showing a positive or negative effect.
- Child well-being: Behavioral and Emotional Functioning: Five contrasts showed a positive effect, two with no effect, and none with a negative effect. All of the five positive effects were reported by Healthy Families Alaska and were fairly large. But all of these were based on the caregiver’s report of the child’s behavior, and self-reports are not sufficient on their own for making conclusions about impact. Moreover, these outcomes and measures were not replicated in any other study.
- Child well-being: social functioning: The Clearinghouse reports no favorable or unfavorable effects and and two contrasts showing no effect.
- Child well-being: cognitive functions and abilities: There were two favorable impacts, one unfavorable impact, and 6 contrasts showing no effect. The two favorable impacts came from Alaska and were not found in any other evaluations.
- Child well-being: physical development and health: The Clearinghouse reported no favorable or unfavorable impacts and six contrasts with no impact.
- Child well-being: delinquent behavior. There was one favorable effect in the one contrast available, which was “child skips school often.” A look at the publication containing this result, which was a report on the RCT of Healthy Families New York (HFNY) seven years after random assignment, showed that fewer children self-reported skipping school, but this result was not supported by reports from their mothers.
- Child well-being: educational attainment: The Clearinghouse reported one favorable impact and two findings of no impact. All three findings came from one publication from the HFNY RCT. The researchers found that children in the HFNY group were about half as likely to be retained in first grade (3.54 percent) than children in the control group (7.10 percent), based on official school data. However, there were no impacts found for the other two educational attainment outcomes used by the Clearinghouse–performing above or below grade level in reading or math. Moreover, this contrast was not available from any other study.
- Adult well-being: positive parenting practices: There were three favorable impacts and 24 findings of no impact. All of the favorable impacts were from another report on HFNY that was based on observations of how the mothers interacted with their children as they completed three tasks–a puzzle solving task, a delay of gratification task, and a cleanup task. I was not able to judge the size of the effects; all were statistically significant at the 0.05 level. However, there were no significant effects on observed presence of harsh parenting during the same tasks. Moreover, this outcome was not included in the evaluation of any other program.
- Adult well-being: parent/caregiver mental/emotional health. The Clearinghouse found three favorable impacts and 16 contrasts showing no impacts from a total of three RCT’s.
- Adult well-being: Parent/Caregiver Substance abuse: There were no favorable or unfavorable effects, and 15 instances where no statistically significant effect was found.
- Adult well-being: family functioning: There were three favorable impacts, one unfavorable impact, and 28 instances of no impact. The three favorable impacts stemmed from three different contrasts related to Intimate Partner Violence (IPV)–overall maternal IPV victimization rate (child age 1-3), maternal IPV victimization rate: physical assault (child aged 1 to 3), and maternal IPV perpetration rate: physical assault (child age 1 to 3). The size of the effect was not provided and there were nine other maternal IPV contrasts when the child was aged 1 to 3 that showed no effect. There were
were no impacts on IPV when the child was older.
- Adult well-being: economic and housing stability. There were no favorable impacts, five contrasts showing no impact, and one showing an unfavorable impact.
Parents as Teachers
The results presented by the Title IV-E Clearinghouse are based on two RCT’s and one study based on a matched comparison group. Even when counting all these programs, the results are not impressive.
- For child safety based on administrative reports, the Clearinghouse noted two contrasts with a favorable effect and two with no effect. The effect size and implied percentile effect calculated by the Clearinghouse were very small. Moreover, these results were based on a matched comparison group rather than an RCT, casting doubt on the validity of the results.
- Child permanency (out-of-home placement): The clearinghouse cited no favorable or unfavorable findings and one finding of no effect.
- Child well-being: social functioning. The original article cited by the Clearinghouse, based on an RCT in two California sites, reported that PAT children in one of the sites benefited significantly, advancing by about two months of the control group in self-help development but did not report significant results for the other site or for social development at either site.
- Child well-being: cognitive functions and abilities: Based on the American and Swiss RCT’s, The Clearinghouse reported two favorable findings and 10 findings of no effect. But one of the findings was actually of no effect for the PAT-only group; it was the “PAT plus case management group” that experienced an impact.
- Child well-being: Physical development and health: The clearinghouse reported no favorable or unfavorable effects and three findings of no effect from one RCT.
- Adult well-being: positive parenting practices: The Clearinghouse reported no favorable or unfavorable effects and one finding of no effect from an RCT.
- Adult well-being: family functioning: The Clearinghouse reported no favorable effects, 8 findings of no effect, and one unfavorable effect, all from one RCT.
- Adult well-being: economic and housing stability. The Clearinghouse reported no favorable effects, one unfavorable effect, and nine findings of no effect, all from one RCT.
SafeCare
SafeCare is a brief home visiting model that is delivered in 18 one-hour sessions. SafeCare is designed for parents and caregivers of children birth through five who are either at-risk for or have a history of child neglect and/or physical abuse.It was included in the Title IV-E Prevention Plans of seven states in April 2023. The contrasts reported by the Clearinghouse include only one favorable effect–on foster care placement–based on a matched comparison group study and not an RCT and one unfavorable effect (on child welfare reports), along with 19 findings of no effect.
Early Head Start Home-based Option
The Early Head Start Home-based option serves low-income women and families with children under three years old. They receive a minimum of weekly 90-minute home visits and two group socialization activities per month. The findings discussed here are based on the HHS Office of Policy Research and Evaluation (OPRE) review of the research on home visiting. OPRE reports that it reviewed 23 “manuscripts” and identified nine of those manuscripts that were based on “impact studies rated high or moderate quality.” By focusing on “manuscripts” instead of studies, OPRE obscured the fact that seven of these manuscripts were actually based on the same study–a large federal demonstration of EHS programs in 17 sites conducted between 1996 and 2002. Of the nine manuscripts, five were based on the full study and two were based on results from one Utah site only. The other two studies reviewed were based on results of the MIHOPE study of four home-visiting models when the children were 15 months old. All but two of the manuscripts were rated high by the OPRE staff in quality for methodology. The manuscripts based on the Utah study and the grade five follow-up for the national study were rated “moderate” in quality because of high attrition. In the nine publications reviewed, there were no favorable findings on maternal or child health; child maltreatment; or delinquency, family violence and crime. There were a few favorable impacts on child development and school readiness; positive parenting practices; and family economic self-sufficiency. These effects were not consistent across age groups or similar outcomes (like reading to children vs. reading at bedtime.) These impacts appeared to be small, although the lack of standardized effect sizes makes the importance of the effects hard to estimate.
- For child development and school readiness, the reviewers reported five favorable findings from the 17-site study and the Utah study. All the other 66 contrasts related to child development and school readiness in the two studies showed no effect. By the time the children in the main study reached fifth grade, no effects remained.
- For positive parenting practices, the reviewers reported 10 favorable findings from the 17-site study and the Utah study. In total, there were 64 findings of no effect in this area. By the time children reached fifth grade, one favorable impact (which was not noted for the three or five year-olds) was observed.
- For family economic self-sufficiency, the reviewers reported 16 favorable findings, one unfavorable finding and 88 findings of no effect from 3 publications in a total of two studies. No economic effects remained by the time the children were in fifth grade.
Appendix II: Home visiting and child maltreatment
Analyzing the effect of any program on child maltreatment poses unique difficulties because it is such a difficult outcome to measure. Obviously, the evaluators cannot see what goes on in a household after the visitor has gone home. Evaluators have used three types of measures to estimate the effects of home visiting programs on child maltreatment–verified child protective services (CPS) reports, health care encounters for injuries or ingestions (or simply emergency room visits), and self-reports of abusive or neglectful behaviors through surveys like the Conflict Tactics Scale.
The most obvious measure of abuse and neglect is official Child Protective Services (CPS) data, but there are several problems with CPS data as a measure of maltreatment. The number of maltreatment reports that are confirmed (substantiated) by CPS is most frequently used, but it is known to be an understatement. Many cases go unreported, and reported cases are often not substantiated. Another problem is that verified abuse is a relatively rare event in a population and a study may not have enough participants to detect it. Finally, h visitors are mandatory reporters and their presence in the home introduces surveillance bias; these families are under more surveillance than families in the control group and may receive more reports for that reason.
Olds and his colleagues did not find statistically significant differences in substantiated CPS reports for the whole program group during the two year period that families participated in the Elmira demonstration or in the subsequent two years. But they found some evidence that the Elmira program did reduce child maltreatment among the participants who were most at risk–those who were teenagers, poor and unmarried. About 19 percent (or a total of eight) of the the poor, unmarried teens had a verified maltreatment report compared to four percent (or one) of their nurse-visited counterparts. But this effect was statistically significant at the p-0.07 level, not the standard level of 0.05. And there were no treatment-control differences in verified maltreatment reports for this subgroup or the whole treatment group during the two years after the program ended. The researchers speculated that this may be due to increased surveillance on the nurse-visited group, because the nurses connected them to other providers before the programs ended.
However, a surprising finding emerged when the children were 15 years old. By that age, nurse-visited children had received on average of 0.29 verified CPS reports compared to 0.54 in the comparison group–a large and highly statistically significant difference. The investigators hypothesized that as young first-time parents mature and develop, small positive changes that [occur while they are in the program] can build and multiply over time, yielding larger effects in later years.” The mechanism by which the Elmira program had such delayed effects is hard to understand. Perhaps it occurred by chance. But in any case, a replication would be necessary to give it credence, and this outcome was not measured in Memphis or Denver.
As an alternative to CPS data, some researchers have used data on health care encounters for children’s injuries or ingestions. Many of these encounters may reflect abuse or neglect but they also would include cases that are not due to either abuse or neglect and would leave out many instances of maltreatment as well. But it is certainly a good indicator of safe parenting. In the four-year followup of the NFP Elmira group, when the children were 25 to 50 months old, the researchers found that nurse-visited children had 40 percent fewer injuries and ingestions (according to notations in their medical records) and and 45 percent fewer notations of or child behavioral or parental coping problems. Nurse-visited children also made 35 percent fewer visits to the emergency room. In the NFP Memphis trial, the evaluators found that nurse-visited children had an average of 0.43 health encounters for injuries or ingestions compared to 0.56 for the control group, or 23 percent fewer encounters in the first two years of their lives. They also spent an average of 0.04 days hospitalized for injuries and ingestions, compared to 0.18 days for the control group. But a more recent evaluation of a large scale implementation of NFP in South Carolina, described above, found no difference found between the experimental and control groups in its composite measure of child mortality and major injury related to abuse or neglect.
Other studies have used parent self-report measures such as the Conflict Tactics Scale. This measure is less valid than the other two because many parents are reluctant to report abusing or neglecting their children. A few studies found positive effects on such measures but without any corroboration from more objective measures.
Notes
This post was edited on November 10, 2025 to add a sentence and links about enrollment and engagement in home visiting and a link to an article about the MIHOPE report.